583. Delete Operation for Two Strings
Problem
Given two strings word1 and word2, return the minimum number of steps required
to make word1 and word2 the same.
In one step, you can delete exactly one character in either string.
Example 1:
Input: word1 = "sea", word2 = "eat"
Output: 2
Explanation: You need one step to make "sea" to "ea" and another step to make "eat" to "ea".
Example 2:
Input: word1 = "leetcode", word2 = "etco"
Output: 4
Constraints:
1 <= word1.length, word2.length <= 500
word1 and word2 consist of only lowercase English letters.
Approach
Tóm tắt đề bài: Cho 2 chuỗi string w1, w2. Mỗi lần ta có thể xoá bớt 1 kí tự bất kì của 1 trong 2 chuỗi.
Tìm số thao tác xoá ít nhất để chuỗi w1 = w2
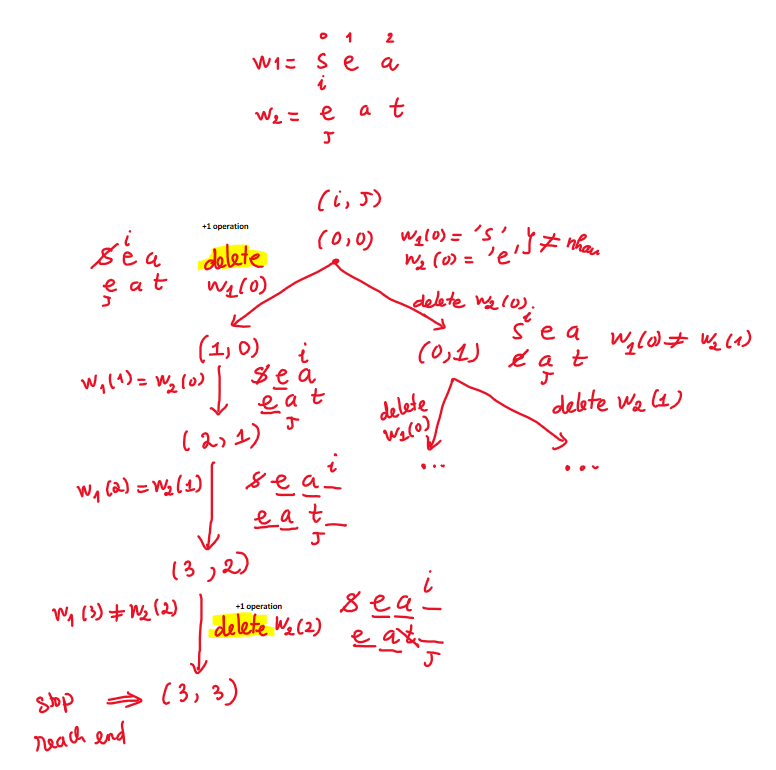 Đọc kĩ đề bài, mỗi lượt ta chỉ có thể có 2 action:
Đọc kĩ đề bài, mỗi lượt ta chỉ có thể có 2 action:
- Xoá một kí tự
- Không làm gì cả
Gọi i, j lần lượt là pointer index của w1 và w2
Ta lần lượt so sánh các kĩ tự w1(i) và w2(j) xem chúng có bằng nhau hay là không? Từ đó lựa chọn action tương ứng (có thể xem hình 1)
Như hình 1, w1(0) != w2(0) nên ta có 2 lựa chọn:
- Xoá kí tự
w1(0). Ta so sánh các kí tự còn lạiw1 = _eavàw2 = eat - Xoá kí tự
w2(0). Ta so sánh các kí tự còn lạiw1 = seavàw2 = _at
Tương tự như vậy cho đến khi i, j tiến tới hết chỗi (i = w1.length và j = w2.length)
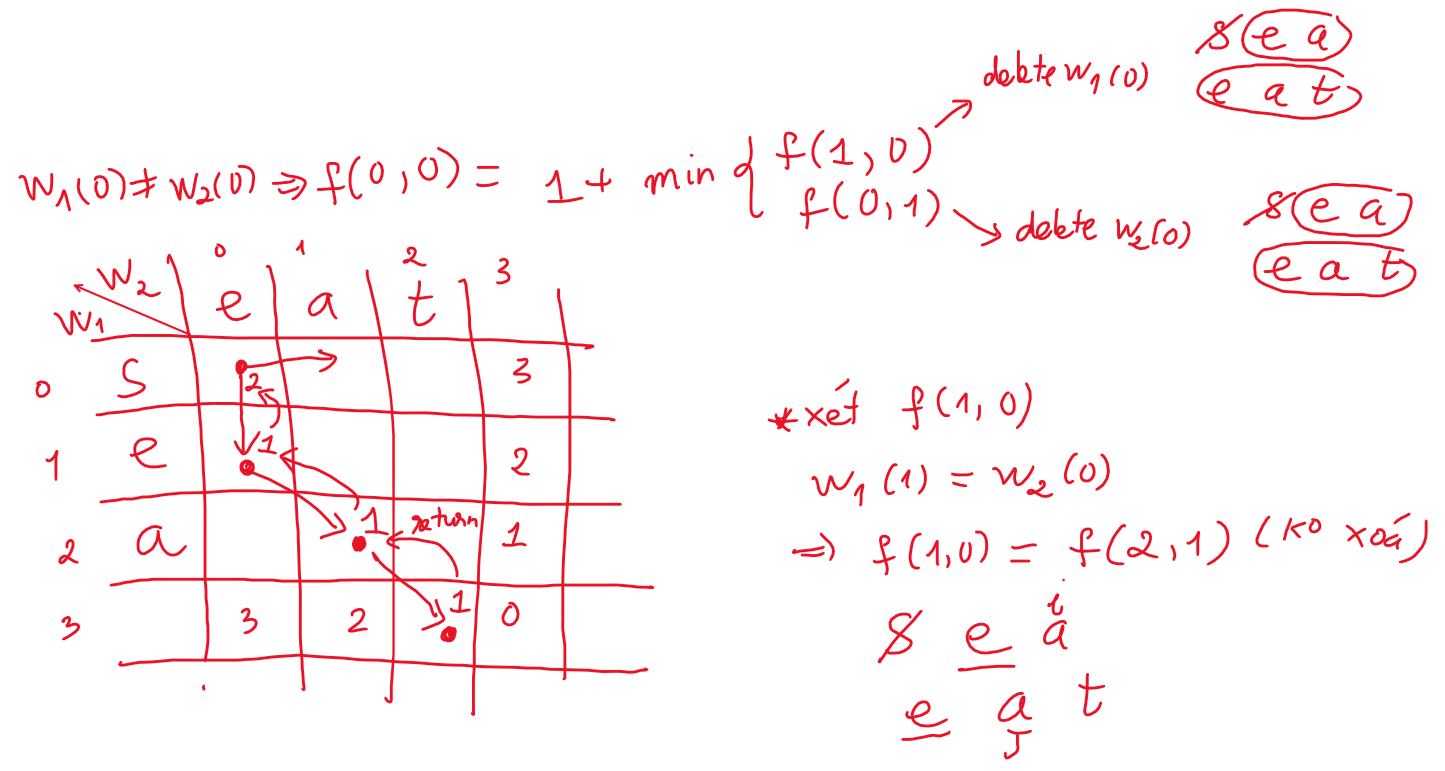 Sau khi giải cách đệ quy ở trên, ta có thể mô hình hoá cách đệ quy ở trên bằng table
Sau khi giải cách đệ quy ở trên, ta có thể mô hình hoá cách đệ quy ở trên bằng table
Với hàm f(i, j) là số operation nhỏ nhất của chuỗi w1[i..end] và w2[j..end]
Và công thức quy hoạch động như hình với 2 trường hợp:
- w1(i) != w2(j) =>
f(i, j) = 1 + min(f(i+1, j), f(i, j+1) -
w1(i) = w2(j) =>
f(i, j) = f(i+1, j+1) - Ngoài ra, vì sao
f(0, 3) = 3. Thì ta cần ít nhất 3 thao tác xoá các kí tựs,e,acủaw1 = seađể w1 trở thànhw2 = _(empty).
Tương tự,f(n, j) = m - j (0 <= j <= m)vàf(i, m) = n - i (0 <= i <= n)vớin = word1.length và m = word2.length
Có thể thấy công thức QHĐ rõ ràng ở phần implementation bên dưới
Implementation
1. Recursion + memorization
class Solution {
private String word1;
private String word2;
private Map<String, Integer> memo;
public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) {
this.word1 = word1;
this.word2 = word2;
this.memo = new HashMap<>();
return dfs(0, 0);
}
private int dfs(int i, int j) {
// base case
if (i == word1.length() && j == word2.length()) {
return 0;
}
String key = i + "_" + j;
if (memo.containsKey(key)) {
return memo.get(key);
}
int ans = 0;
// case: w1(i) = w2(j) => both increase (i,j)
if (i < word1.length() && j < word2.length()
&& word1.charAt(i) == word2.charAt(j)) {
ans = dfs(i+1, j+1);
}
// case: w1(i) != w2(j)
else {
if (i == word1.length()) {
ans = 1 + dfs(i, j+1); // delete w2(j) => increase j
} else if (j == word2.length()) {
ans = 1 + dfs(i+1, j); // delete w1(i) => increase i
} else {
// delete w1(i) or delete w2(j)
ans = 1 + Math.min(dfs(i+1, j), dfs(i, j+1));
}
}
memo.put(key, ans);
return ans;
}
}
Dynamic programming
class Solution {
public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) {
int n = word1.length(); int m = word2.length();
int[][] dp = new int[n+1][m+1];
dp[n][m] = 0;
for (int r = 0; r < n; r++) {
dp[r][m] = n - r;
}
for (int c = 0; c < m; c++) {
dp[n][c] = m - c;
}
for (int i = n-1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = m-1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (word1.charAt(i) == word2.charAt(j)) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i+1][j+1];
} else {
dp[i][j] = 1 + Math.min(dp[i+1][j], dp[i][j+1]);
}
}
}
return dp[0][0];
}
}