72. Edit Distance
Problem
Given two strings word1 and word2, return the minimum number of
operations required to convert word1 to word2.
You have the following three operations permitted on a word:
Insert a character
Delete a character
Replace a character
Example 1:
Input: word1 = "horse", word2 = "ros"
Output: 3
Explanation:
horse -> rorse (replace 'h' with 'r')
rorse -> rose (remove 'r')
rose -> ros (remove 'e')
Example 2:
Input: word1 = "intention", word2 = "execution"
Output: 5
Explanation:
intention -> inention (remove 't')
inention -> enention (replace 'i' with 'e')
enention -> exention (replace 'n' with 'x')
exention -> exection (replace 'n' with 'c')
exection -> execution (insert 'u')
Constraints:
0 <= word1.length, word2.length <= 500
word1 and word2 consist of lowercase English letters.
Approach
Tóm tắt đề bài: Cho 2 chuỗi string w1, w2. Tìm số operations nhỏ nhất có thể convert w1 thành w2. Các operations có thể thực hiện trên chuỗi w1:
- Chèn thêm 1 kí tự mới
- Xoá 1 kí tự
- Thay thế 1 kí tự bất kì w1(i) thành 1 kí tự bất kì
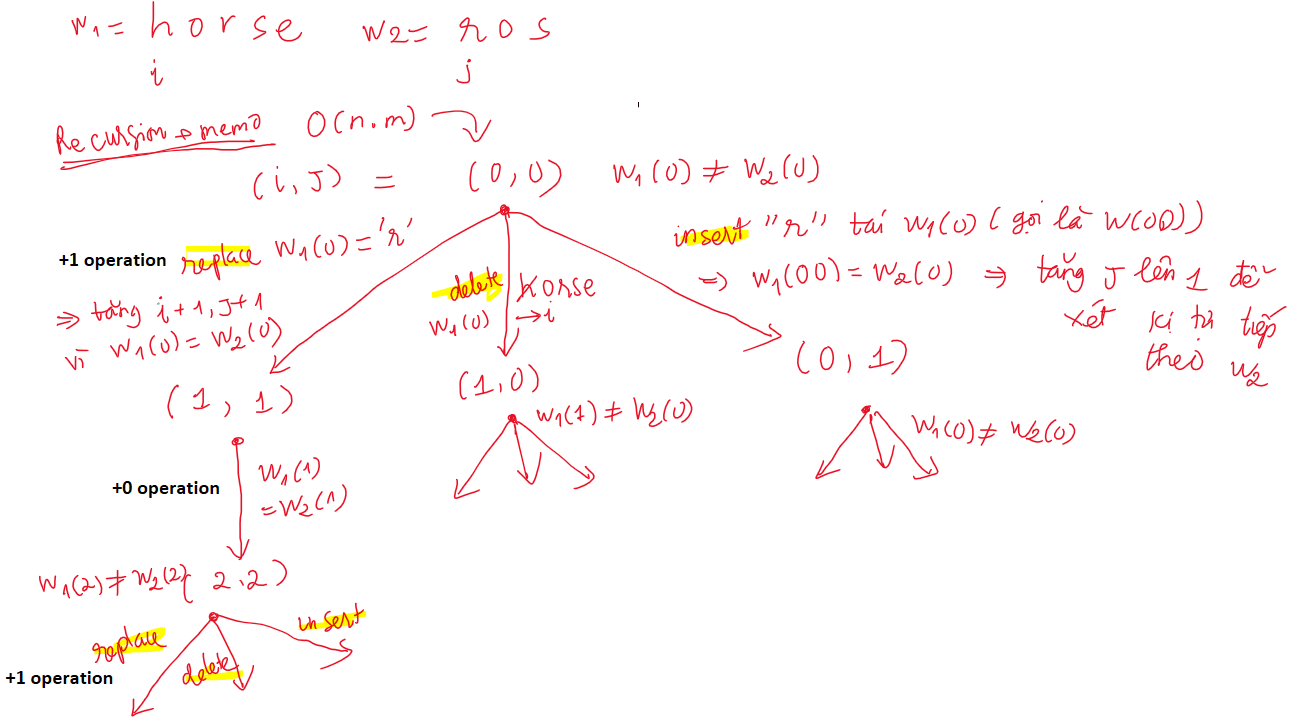 Gọi
Gọi i, j lần lượt là pointer index của w1 và w2
Gọi dfs(i,j) là số operations nhỏ nhất để biến w1[i..n] thành w2[j..m] với n, m lần lượt là chiều dài của w1, w2
Ta lần lượt so sánh các kĩ tự w1(i) và w2(j) xem chúng có bằng nhau hay là không? Từ đó lựa chọn action tương ứng (có thể xem hình 1)
Như hình 1, w1(0) != w2(0) nên ta có 3 lựa chọn:
- Replace
w1(0)thànhr=>tăng i, j lên 1vì sau operation này thì w1(0) = w2(0) - Delete
w1(0) = h=>chỉ tăng i lên 1, j giữ nguyênvì ta vẫn cần so sánh kí tự tiếp theo w1(i+1) với w2(j) - Insert kí tự
rtrước vị tríw1(0)=>giữ nguyên i, chỉ tăng j lên 1vì lúc nàyw2(0) = kí tự 'r' vừa insert ở w1
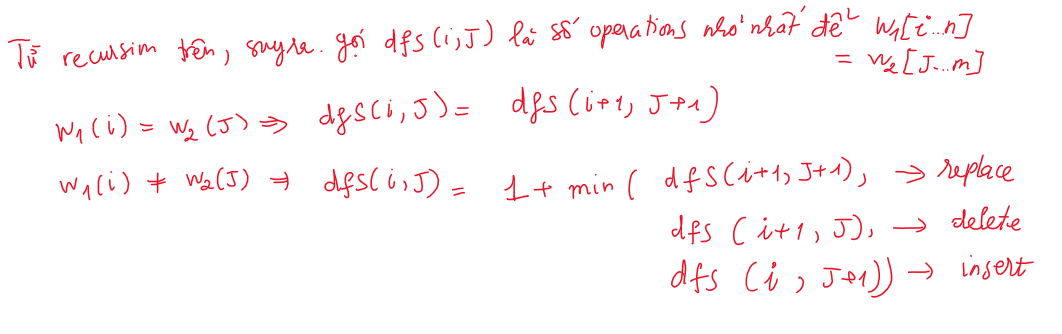 Từ cây đệ quy trên, ta dễ dàng tìm được công thức quy hoạch động hoặc là công thức đệ quy Gọi
Từ cây đệ quy trên, ta dễ dàng tìm được công thức quy hoạch động hoặc là công thức đệ quy Gọi dfs(i,j) là số operations nhỏ nhất để biến w1[i..n] thành w2[j..m] với n, m lần lượt là chiều dài của w1, w2 \
-
dfs(i, j) = dfs(i+1, j+1)nếu w1(i) = w2(j) -
dfs(i, j) = 1 + min(dfs(i+1, j+1), dfs(i+1, j), dfs(i, j+1))nếu w1(i) != w2(j)
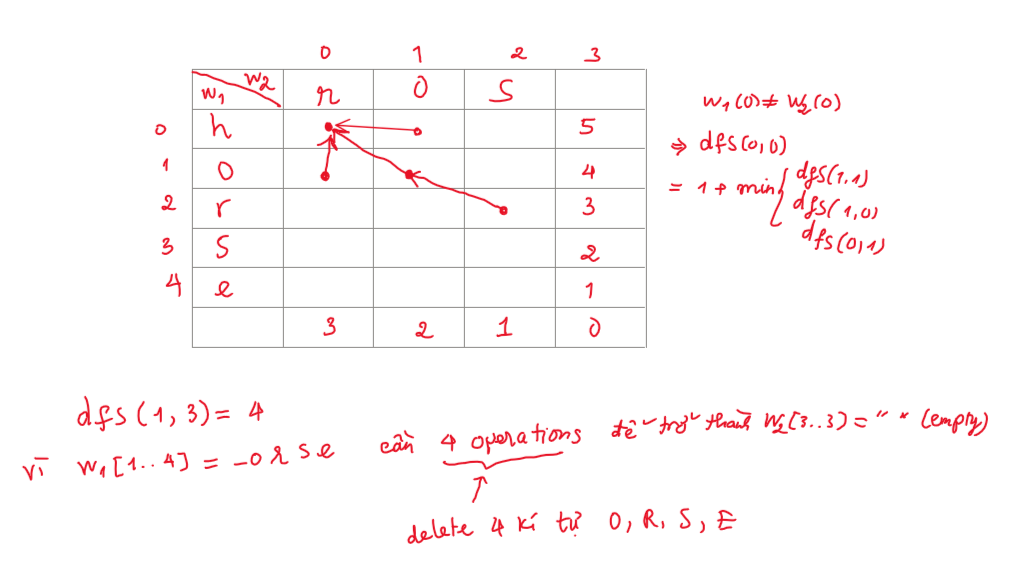 Với công thức đệ quy ở trên, ta dễ dàng biến cấu trúc cây đệ quy trên thành dạng bảng như hình Ngoài ra, như hình trên ta có các
Với công thức đệ quy ở trên, ta dễ dàng biến cấu trúc cây đệ quy trên thành dạng bảng như hình Ngoài ra, như hình trên ta có các base case, với ví dụ dfs(1,3) = 4 đã được giải thích trên hình
Implementation
1. Recursion + memorization
class Solution {
private String w1;
private String w2;
private Map<String, Integer> memo;
public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) {
this.w1 = word1;
this.w2 = word2;
this.memo = new HashMap<>();
return dfs(0, 0);
}
private int dfs(int i, int j) {
// base case
if (i == w1.length() && j == w2.length()) {
return 0;
}
// if reach end w1
// => insert all remaining characters of w2 into w1 to make w1 = w2
if (i == w1.length()) {
return w2.length() - j; // insert remaining characters of w2
} else if (j == w2.length()) {
// if reach end w2
// => delete all remaining character of w1 to make w1 = w2
return w1.length() - i; // delete all remaining characters of w1
}
String key = i + "_" + j;
if (memo.containsKey(key)) {
return memo.get(key);
}
int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if (w1.charAt(i) == w2.charAt(j)) {
ans = dfs(i+1, j+1);
} else {
ans = 1 + min(
dfs(i+1, j+1), // replace
dfs(i+1, j), // delete
dfs(i, j+1) // insert
);
}
memo.put(key, ans);
return ans;
}
private static int min(int a, int b, int c) {
return Math.min(a, Math.min(b, c));
}
}
Dynamic programming
class Solution {
/**
* After solved problem by using recursion + memo => just transform it to dp easily
*/
public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) {
int n = word1.length(); int m = word2.length();
int[][] dp = new int[n+1][m+1];
// base case
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
dp[i][m] = n - i;
}
for (int j = 0; j <= m; j++) {
dp[n][j] = m - j;
}
// dp
for (int i = n-1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = m-1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (word1.charAt(i) == word2.charAt(j)) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i+1][j+1];
} else {
dp[i][j] = 1 + min(
dp[i+1][j+1], // replace
dp[i+1][j], // delete
dp[i][j+1] // insert
);
}
}
}
return dp[0][0];
}
private static int min(int a, int b, int c) {
return Math.min(a, Math.min(b, c));
}
}